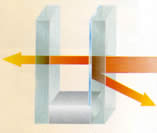
 How Does Low-E Glass Work
How Does Low-E Glass Work
Low-E glass has a special metal coating on one side – either Pyrolytic (hard coat) or sputtered (soft coat). The microscopically thin and almost invisible coating acts as a filter blocking long wave radiation (e.g. infrared heat) and letting in short ave radiation (e.g. UV and visible light).
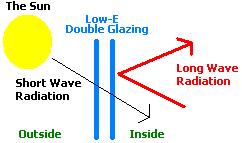
When the Sun’s short wave radiation passes through a window into a room, it is absorbed by the furniture and carpets in the room. Here that energy is transformed into long wave radiation (thermal radiation) in the form of heat – i.e. the sun warms up the furniture and carpets in the room.

During the winter, heat (long wave radiation) in the room naturally wants to escape through the glass, but low-E glass reflects it back into the room keeping it warm. If you touch a standard pane of glass in the winter it feels very cold, even if the room itself is hot. If you touch the inner pane of Low-E glass, it feels much much warmer.
During the summer months it is hot outside, but the low-E glass does not let the infrared thermal radiation (long wave) pass through it reducing the overall solar heat gain of the building.
How is Low-E Glass Manufactured
There are two types of Low-E Glass – Hard Coat and Soft Coat.
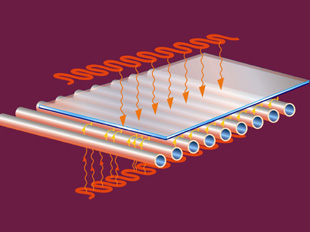
Hard Coat Low-E glass has a thin layer of molten tin poured over it while the glass is still slightly molten. The tin welds to the glass making the coating very strong and difficult to scratch or remove.
Soft Coat Low-E glass has silver, zinc, or tin applied to it in a vacuum chamber filled with an electrically charged inert gas. Atoms of the coating metal are sputtered onto the surface of the glass where they stick.
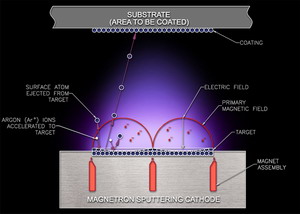
This coating is very easy to scratch, therefore the coated side is always used on one of the inner faces of the double glazing where the argon gas held between the two panes of glass prevents oxidisation.
Soft Coat Low-E glass has better insulating qualities than Hard Coat Low-E glass. In double glazing units filled with inert argon, the R value (measure of resistance to heat loss) is 4.35 for soft coat, and 2.75 for hard coat. A single pane of regular glass would have an R value of below 1.